Essential Considerations for Handicap Bathroom Layout Design

Creating accessible bathroom spaces is crucial for ensuring inclusivity and providing a comfortable experience for all individuals. The design of handicap bathrooms must prioritize functionality and safety, taking into account the needs of people with disabilities.
ADA Guidelines and their Impact on Bathroom Design
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provides comprehensive guidelines for accessible design, ensuring that people with disabilities can access and use public and private facilities. These guidelines cover various aspects of bathroom design, including dimensions, clearances, and features. Adherence to ADA standards is essential for creating compliant and accessible bathrooms.
Universal Design Principles in Creating Accessible Spaces
Universal design principles emphasize creating spaces that are usable and enjoyable by individuals with diverse abilities and needs. This approach goes beyond mere compliance with ADA standards, aiming to create a welcoming and inclusive environment for everyone. Key principles of universal design include:
- Flexibility in Use: Designing features that can be used in multiple ways, accommodating a wide range of abilities and preferences.
- Simple and Intuitive Use: Creating straightforward and easy-to-understand interfaces and controls, minimizing the need for instructions or special knowledge.
- Perceptibility: Ensuring that information and features are easily perceived by all users, regardless of sensory abilities. This includes providing clear visual cues, audible warnings, and tactile markings.
- Tolerance for Error: Designing features that minimize the potential for errors and provide clear feedback to users. This includes providing safeguards and redundancy to prevent accidents.
- Low Physical Effort: Minimizing the physical exertion required to use facilities, ensuring accessibility for individuals with limited strength or mobility.
- Size and Space for Approach and Use: Providing adequate space for maneuvering and accessing features, considering the use of mobility aids.
- Clear Lines of Sight: Ensuring that users have unobstructed views of their surroundings, facilitating navigation and safety.
Accessibility Features for Handicap Bathrooms
Handicap bathrooms often incorporate various features to enhance accessibility and safety. Some common features include:
- Grab Bars: Strategically placed grab bars provide support for individuals who need assistance with balance or stability. These bars should be securely mounted and positioned at appropriate heights for different users.
- Roll-in Showers: Roll-in showers allow wheelchair users to access the shower without having to transfer. They typically have a level entry, a wide door opening, and a shower seat for comfort and safety.
- Lowered Sinks: Sinks that are lowered to a height accessible for wheelchair users are essential for maintaining independence in personal hygiene.
- Accessible Toilets: Toilets should be mounted at a lower height to allow for easier access and use. They should also have sufficient clearance for wheelchair users to maneuver around them.
- Accessible Mirrors: Mirrors should be positioned at a height accessible for wheelchair users, ensuring they can see themselves clearly.
- Accessible Water Controls: Water controls should be easy to reach and operate, considering the needs of individuals with limited dexterity.
- Accessible Door Hardware: Door handles and latches should be easy to grasp and operate, accommodating individuals with limited hand strength or dexterity.
Types of Mobility Aids and their Influence on Layout Design
The layout of a handicap bathroom should consider the various types of mobility aids used by individuals with disabilities.
- Wheelchairs: Wheelchair users require sufficient turning radius and clearance for maneuvering around the bathroom. This includes providing wide doorways, adequate aisle widths, and clear access to all features.
- Walkers: Individuals using walkers need adequate space to maneuver and turn, ensuring sufficient aisle widths and clearance around fixtures.
- Canes: Cane users need adequate space to navigate, ensuring that there are no obstacles or clutter that could hinder their movement.
Minimum Dimensions for Handicap Bathroom Features
The ADA establishes minimum dimensions for various bathroom features to ensure accessibility. The following table Artikels some key dimensions:
| Feature | Minimum Dimension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Clear Floor Space in Front of Toilet | 30 inches (76 cm) | Minimum clear space required for wheelchair users to transfer to and from the toilet. |
| Clear Floor Space in Front of Sink | 30 inches (76 cm) | Minimum clear space required for wheelchair users to access the sink. |
| Doorway Width | 32 inches (81 cm) | Minimum width required for wheelchair access. |
| Turning Radius | 60 inches (152 cm) | Minimum turning radius required for wheelchair users to maneuver in the bathroom. |
| Grab Bar Height | 33-36 inches (84-91 cm) | Recommended height for grab bars to provide support for different users. |
Optimizing Space and Functionality
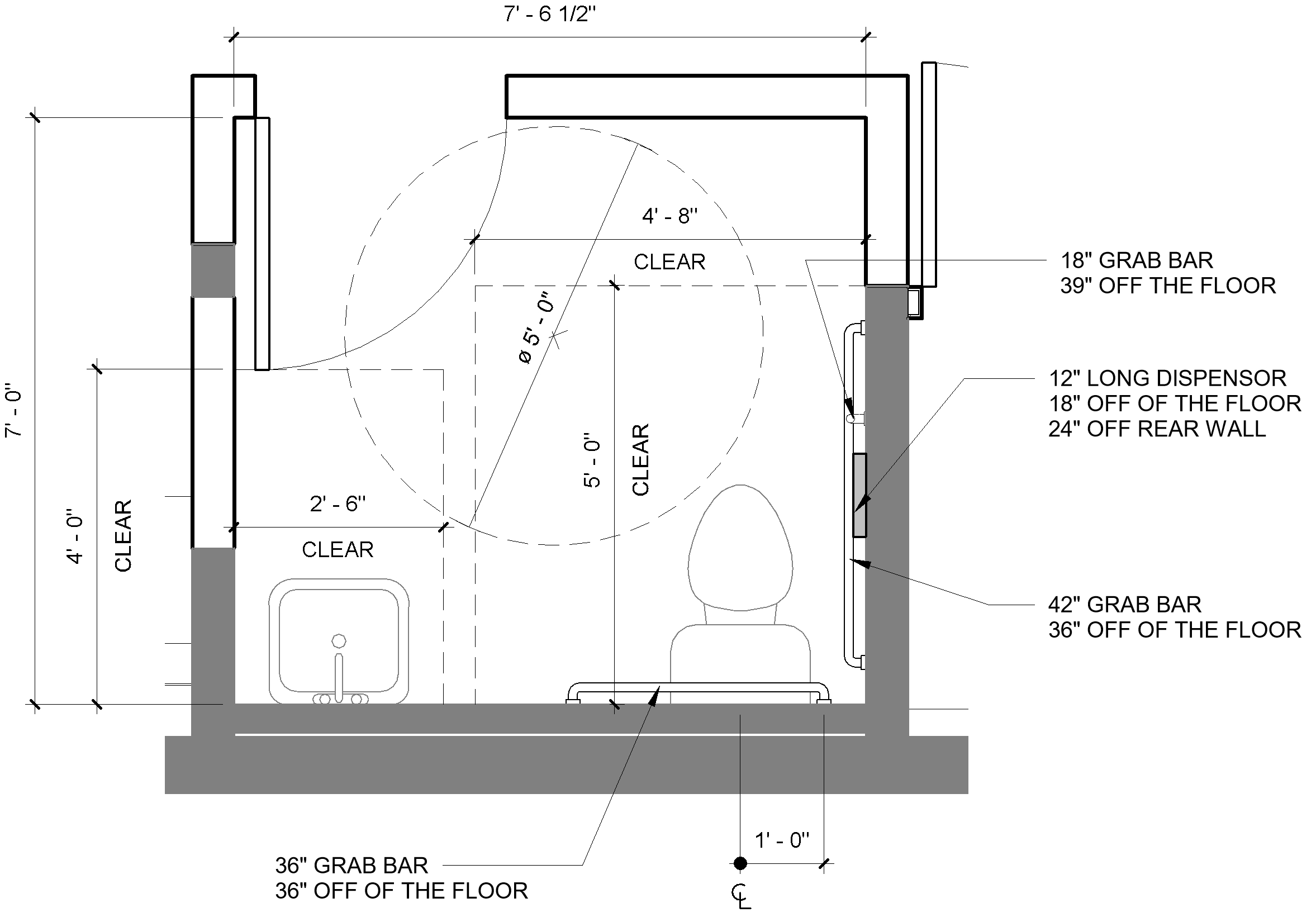
Creating a handicap bathroom that is both functional and comfortable requires careful planning and consideration of the user’s needs. Optimizing space utilization is crucial in maximizing accessibility and ease of movement.
Clear Pathways and Turning Radii
Clear pathways and adequate turning radii are essential for wheelchair users to navigate the bathroom safely and independently. The minimum width for a wheelchair-accessible pathway is 36 inches, with a 60-inch turning radius. This allows for comfortable maneuvering and avoids potential collisions with fixtures or walls.
Maximizing Space Utilization in Small Bathrooms
Small bathrooms can be challenging to design for accessibility. However, several strategies can help maximize space utilization:
- Compact Fixtures: Choosing compact toilets, sinks, and showers can free up valuable floor space.
- Wall-Mounted Fixtures: Wall-mounted sinks and toilets can increase floor space and facilitate easier cleaning.
- Corner Sinks: Corner sinks effectively utilize space in small bathrooms and provide ample counter space.
- Sliding Doors: Sliding doors require less space to open and close, compared to swinging doors.
Different Layout Configurations for Handicap Bathrooms, Handicap bathroom layout design
There are several layout configurations that can optimize space and functionality in handicap bathrooms. These include:
- L-Shaped: An L-shaped layout provides a clear pathway for wheelchair users, with the toilet and sink located on adjacent walls. This configuration is suitable for small bathrooms.
- U-Shaped: A U-shaped layout offers more space and allows for the placement of fixtures on three walls, creating a more spacious and accessible environment.
- Linear: A linear layout places fixtures in a straight line, which can be an effective option for long, narrow bathrooms. This configuration ensures easy accessibility for wheelchair users.
Role of Lighting in Handicap Bathrooms
Proper lighting is essential for creating a safe and comfortable environment in handicap bathrooms. Adequate lighting ensures visibility and reduces the risk of accidents.
- Task Lighting: Task lighting, such as overhead fixtures and under-cabinet lights, should be sufficient to illuminate key areas like the sink and toilet.
- Ambient Lighting: Ambient lighting, such as wall sconces or recessed lights, can create a more relaxing atmosphere.
- Avoid Glare: Avoid using bright, reflective surfaces that can create glare and make it difficult to see.
Typical Handicap Bathroom Layout
| Feature | Dimensions | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Clear Pathway | 36 inches wide | Provides sufficient space for wheelchair maneuvering. |
| Turning Radius | 60 inches diameter | Allows for safe and comfortable turning. |
| Toilet | 18 inches from wall | Placed at an accessible height for easy transfer. |
| Grab Bars | 32 inches high, 1 1/2 inches diameter | Installed near the toilet and shower for support. |
| Sink | 34 inches high, 30 inches wide | Accessible height and ample counter space. |
| Shower | 36 inches wide, 36 inches deep | Roll-in shower with a non-slip surface. |
Handicap bathroom layout design is crucial for accessibility and safety, especially considering the potential for water damage. Ensuring proper ventilation is key, which can be achieved through strategically placed exhaust fans. However, even with good ventilation, moisture can accumulate, leading to the growth of mold.
This is where selecting the right bathroom ceiling mould paint becomes essential. Choosing a mold-resistant paint not only protects the ceiling but also contributes to a healthier environment, which is particularly important in a handicap bathroom where individuals may have compromised immune systems.
Handicap bathroom layout design prioritizes accessibility and safety, often incorporating features like grab bars and wider doorways. While functionality is paramount, a touch of personality can be added through thoughtful design choices. A vibrant hue like mustard colour bathroom paint can infuse the space with warmth and cheer, making it feel more welcoming and less clinical.
Ultimately, the key is to create a bathroom that is both practical and aesthetically pleasing, ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable experience for all users.